Spiritual Awakening Iboga’s Connection to Nature
- In the heart of our bustling world, where the pace of life often overwhelms the spirit, there exists a sacred plant known as Iboga—an ancient gift from Mother Nature herself. This plant, native to the rainforests of Central Africa, carries within its roots the key to profound healing and spiritual awakening. Iboga, revered by indigenous cultures for centuries, is more than a medicinal plant; it’s a gateway to the realms of the soul and a bridge to the wisdom of the natural world. Here’s how Iboga healing beautifully intertwines with spirituality and our connection to nature:
- 1. Communion with the Earth: Iboga journeys often take place in natural settings, allowing individuals to immerse themselves in the embrace of the Earth. The sights, sounds, and energies of the forest or wilderness become partners in the healing process, reinforcing our bond with the natural world.
- Spiritual Awakening: Iboga is known for its potential to induce profound spiritual experiences. It can reveal hidden truths, illuminate the path to self-discovery, and foster a sense of interconnectedness with all living beings—a realization that echoes the spiritual teachings found in nature.
- Mind-Body-Spirit Alignment: Iboga healing is not just about physical well-being; it aligns the mind, body, and spirit. Through introspection and guidance, individuals can release emotional baggage, find inner balance, and rekindle their spiritual connection.
- Lessons from Nature: Iboga teaches us to honor the wisdom of the natural world. It reminds us that our existence is intricately woven into the fabric of the Earth, and by respecting nature, we honor the sacred cycles of life.
- Personal Transformation: The journey with Iboga is often described as a “rebirth.” It offers a chance to shed old layers, heal wounds, and emerge as a more authentic and spiritually attuned individual, much like the cycles of growth and renewal observed in nature.
- In the nurturing arms of Iboga, individuals embark on a profound spiritual journey, reconnecting with the timeless rhythms of the Earth. It is a reminder that true healing often lies not just in medicine but in the embrace of nature’s wisdom—a wisdom that has the power to rekindle our spirits and lead us back to the heart of our truest selves.

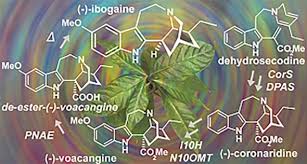
VOACANGA AFRICANA. HEALING WONDERS OF A BOTANICAL TREASURE FROM WEST AFRICA
Nestled within the enchanting landscapes of West Africa, the Voacanga Africana tree emerges as a captivating botanical wonder, revered for its age-old medicinal virtues. With roots that delve deep into traditional healing practices and branches that extend toward modern scientific exploration, Voacanga offers a tapestry of potential applications that beckon exploration. Let’s embark on a journey to explore the virtues and applications of this remarkable plant.
A Botanical Revelation: The Mystique of Voacanga africana
Voacanga africana, a member of the Apocynaceae family, possesses a rich pharmacological profile that has piqued the curiosity of scientists and herbalists alike. Its bark, seeds, and roots house a trove of alkaloids, notably voacangine, voacamine, and tabersonine. These compounds, found in varying concentrations across different plant parts, are believed to hold the key to Voacanga’s potential medicinal properties.
Traditional Wisdom Meets Modern Discovery:
For centuries, Voacanga has played a vital role in traditional healing practices across West Africa. Its alkaloids have been harnessed for their reported analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and stimulant effects. In traditional settings, Voacanga preparations have been used to address various ailments, from pain management to boosting vitality.

Unraveling the Virtues: Potential Applications of Voacanga africana
- Relieving Pain, Naturally: The alkaloids within Voacanga have been traditionally revered for their analgesic attributes. They have been utilized to alleviate pain, making it a cherished companion in addressing discomfort.
- Energy and Vitality Unleashed: In the bustling rhythms of modern life, fatigue can be a constant companion. Voacanga’s stimulant properties have led to its reputation as a natural energizer, offering respite from weariness and a renewed zest for life.
- Harnessing Nature’s Anti-Inflammatory Power: Echoes of tradition suggest that Voacanga might harbor potent anti-inflammatory potential. As modern science delves into this aspect, Voacanga might find its niche in supporting inflammatory conditions.
Navigating with Care: The Balance of Potential and Responsibility
Within Voacanga’s offerings lies a realm of promise, yet this realm is adorned with cautionary signposts. Its alkaloids possess a formidable influence over the central nervous system—a reminder to tread carefully. Respect and informed guidance are non-negotiables when approaching the healing possibilities of Voacanga.
Charting New Frontiers: A Botanical Odyssey Continues
As our collective fascination with botanicals blossoms, Voacanga africana takes center stage. Researchers illuminate its chemical complexities, unravel its mechanisms, and explore its potential in modern therapeutics. However, this journey, akin to the tree’s own growth, is an ongoing process that demands patience, curiosity, and a commitment to nurturing nature’s gifts responsibly.
Harmony Between Botany and Healing
In conclusion, Voacanga africana stands as a testament to the intricate relationship between nature and healing. Its presence in traditional practices and its potential in modern applications highlight the enduring relevance of botanical wisdom. As we unravel the mysteries of Voacanga, let us do so with reverence, curiosity, and a commitment to responsible exploration.
Understanding addiction
Breaking the Stigma and Promoting Empathy
Understanding the science behind addiction is crucial in dispelling misconceptions and promoting empathy. Addiction affects the brain’s chemistry, leading to changes in behavior and decision-making. Whether it’s alcohol, prescription pain pills, nicotine, gambling, or something else, overcoming an addiction isn’t as simple as just stopping or exercising greater control over impulses. By delving into the science behind addiction, we can gain a deeper understanding of its mechanisms, break down stigmas, and promote empathy and support for those battling addiction. Addiction occurs when the brain’s pleasure pathways become overwhelmed, leading to a persistent and potentially long-lasting condition. Let’s explore the key elements together.
The Science of Addiction
- The Brain and Addiction
The relationship between the brain and addiction is a complex and intricate one. Addiction involves changes in the brain’s structure and function that contribute to compulsive drug-seeking and drug use behaviors. Understanding this relationship can shed light on why addiction is such a challenging and chronic condition.
The brain plays a crucial role in regulating our behavior, emotions, and decision-making processes. It consists of various regions and circuits that communicate with each other through chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. One such neurotransmitter that is closely associated with addiction is dopamine.
Dopamine is involved in the brain’s reward system, which is responsible for experiencing pleasure and reinforcing behaviors necessary for survival, such as eating and bonding. When we engage in pleasurable activities, including using drugs, dopamine is released, creating a sensation of reward and reinforcing the behavior.
In the case of addiction, repeated drug use can hijack the brain’s reward system. Drugs of abuse, such as opioids, stimulants, or alcohol, can artificially increase dopamine levels, leading to intense feelings of euphoria. Over time, the brain adapts to these elevated dopamine levels by reducing its natural production of dopamine or altering the sensitivity of dopamine receptors.
These changes in the brain’s reward system can result in several significant effects. Firstly, individuals may develop a tolerance to the drug, requiring higher doses to achieve the same level of reward. This tolerance can lead to increased drug consumption and escalate the risk of addiction.
Secondly, the brain’s prefrontal cortex, responsible for decision-making, impulse control, and judgment, may become impaired in individuals with addiction. This can contribute to the inability to resist drug cravings and make rational choices regarding drug use.
Additionally, the brain’s stress and emotional regulation systems can become dysregulated in addiction. Chronic drug use can disrupt the brain’s natural balance, leading to heightened stress responses, emotional instability, and an increased susceptibility to relapse.
It’s important to note that addiction is not solely a result of weak willpower or moral failing. It is a complex brain disorder that involves both biological and environmental factors. Genetic predisposition, environmental stressors, and social influences can all contribute to the development and progression of addiction.
By understanding the relationship between the brain and addiction, we can recognize addiction as a chronic brain disorder that requires comprehensive treatment and support. Effective interventions involve addressing both the biological and psychosocial aspects of addiction to promote recovery and long-term well-being.
As a result of scientific research, we know that addiction is a medical disorder that affects the brain and changes behavior. We have identified many of the biological and environmental risk factors and are beginning to search for the genetic variations that contribute to the development and progression of the disorder. Scientists use this knowledge to develop effective prevention and treatment approaches that reduce the toll drug use takes on individuals, families, and communities.
Author NaNora D. Volkow, M.D.
Director
National Institute on Drug Abuseme
The use of Ibogaine
– A Testimony of Hope and Healing in Addiction Recovery with the use of Ibogaine
In the journey of addiction recovery, individuals often seek various treatment options to find solace and reclaim their lives. One intriguing approach that has gained attention is the use of Ibogaine, a plant-derived psychedelic substance known for its potential therapeutic effects. Explore this compelling testimony highlighting the transformative power of Ibogaine in addiction treatment.
Addiction can be an overwhelming and challenging battle, but for those who have experienced the depths of its grip, hope can come in unexpected forms. Recently, we came across a remarkable testimony that shed light on the potential of Ibogaine, an alternative treatment option for addiction recovery. The testimony shared the story of Amber Capone, who found renewed hope and healing through Ibogaine therapy.
Before diving into the testimony, it’s important to understand what Ibogaine is and how it works. Derived from the root bark of the Iboga plant, Ibogaine is a psychedelic substance known for its unique properties. It has been reported to provide profound introspection, reduce cravings, and interrupt the cycle of addiction. However, it’s crucial to note that Ibogaine therapy should only be administered under professional supervision due to its potential risks and side effects. Read more on Ibogaine as a treatment for substance misuse here
Amber Capone had become afraid of her husband. The “laid-back, bigger than life and cooler than cool” man she’d married had become isolated, disconnected and despondent during his 13 years as a U.S. Navy SEAL. Typically, he was gone 300 days of the year, but when he was home, Amber and their two children walked on eggshells around him. “Everyone was just playing nice until he left again,” Amber says on Time.com.
In 2013, Marcus retired from the military. But life as a civilian only made his depression, anger, headaches, anxiety, alcoholism, impulsivity and violent dreams worse. Sometimes he’d get upset by noon and binge-drink for 12 hours. Amber watched in horror as his cognitive functioning declined; Marcus was in his late 30s, but he would get lost driving his daughter to volleyball, and sometimes he couldn’t even recognize his friends. Psychologists had diagnosed him with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression and anxiety, but antidepressants, Ambien and Adderall didn’t help. He visited a handful of brain clinics across the country, which diagnosed him with postconcussive syndrome after a childhood of football—then a career punctuated by grenades, explosives, rifles and shoulder-fired rockets. But all they offered were more pills, none of which helped either. Marcus wasn’t the only one suffering in his tight-knit community of Navy SEALs and special-operations veterans. A close friend killed himself, and Amber knew her husband could be next. “I truly thought that Marcus would be the one having the suicide funeral,” Amber says. There was one last option. One of Marcus’ retired Navy SEAL friends, who had similarly struggled, had traveled internationally to take ibogaine, a psychedelic drug illegal in the U.S. The ibogaine experience had been transformative for him, and he thought it might be the same for Marcus. “I thought it was crazy,” Marcus says. “How can you take another pill to solve all your problems?” But Amber begged him to try it, and Marcus gave in. On Veterans Day in 2017, Marcus checked into a treatment center in Mexico, popped an ibogaine pill, slipped on eyeshades and noise-canceling headphones, and went on his first-ever psychedelic trip. After an hour or so, he entered a waking dream state and watched a movie of his life play out before his eyes. It lasted 12 hours, and it was awful at times. “Imagine some of the worst experiences of your life,” Marcus says. “You’re going to experience these again.” Life events flipped through his mind’s eye in rapid fire. Other times, painful memories slowed to a crawl. Marcus saw himself having conversations with his dead father, with buddies he’d lost to the wars over the years, with God. “You can’t hide from the medicine,” he says. “It’s just going to go down there and basically pull up any traumas, anything hiding in your subconscious that may be affecting you that you don’t even realize.” When it was over, Marcus felt as if he’d finally put down a heavy load he’d been carrying for years. For the first time in a long time, he didn’t want a drink, and he didn’t touch alcohol for a year after. “I was thinking clear. I wasn’t impulsive anymore. I had no anxiety. I wasn’t depressed,” he says. Amber couldn’t believe it, but when she picked him up, she knew she had her husband back. “When he walked into the room, it was as though I was witnessing him the first time I met him,” she says. “His anger and his darkness and his whole demeanor had changed. All of that was gone. He was easy. He was light. He was present. He was happy. It just absolutely blew my mind.”
The testimony of Amber Capone serves as a poignant reminder of the multifaceted nature of addiction and the potential for alternative treatments to offer hope and healing. Personal stories like this one can inspire individuals who are struggling with addiction, providing a glimmer of light and a sense of possibility for their own recovery journeys.
While Ibogaine therapy shows promise in the realm of addiction recovery, it’s essential to approach it with caution, seeking guidance from medical professionals and addiction specialists. Personal testimonies can shed light on the potential benefits of alternative treatments, but it’s crucial to remember that every individual’s journey is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another.
By sharing stories like that of Amber, we aim to raise awareness, spark conversations, and provide individuals with a broader understanding of the options available in their pursuit of addiction recovery.
STRATEGIES FOR ADDICTION RECOVERY
On the path to overcoming addiction, self-care becomes an invaluable ally, offering support, strength, and resilience. This blog post delves into the realm of self-care strategies tailored for individuals navigating the challenges of addiction recovery. Explore a range of empowering practices designed to help you manage cravings, improve emotional well-being, and foster a healthy and fulfilling lifestyle. By prioritizing self-care, you can enhance your journey towards healing and transformation.
- Establish a Supportive Routine: Creating a structured and supportive routine is crucial for addiction recovery. Set regular sleeping patterns, incorporate nutritious meals, and establish a schedule that includes exercise and self-care activities. Consistency and routine provide stability and a sense of purpose, aiding in managing triggers and cravings.
- Engage in Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation can significantly support addiction recovery. These techniques help you develop awareness of your thoughts, emotions, and cravings without judgment. By cultivating mindfulness, you can increase self-awareness, manage stress, and build resilience in the face of challenges.
- Prioritize Physical and Emotional Well-being: Engaging in physical exercise not only benefits your physical health but also plays a vital role in addiction recovery. Regular exercise helps reduce stress, promotes a positive mood, and boosts self-esteem. Additionally, explore therapeutic activities like yoga, deep breathing exercises, or journaling to improve emotional well-being and enhance self-reflection.
- Cultivate Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Replace unhealthy coping mechanisms with positive alternatives. Explore activities such as art therapy, music therapy, or nature walks to channel your emotions and express yourself. Engaging in creative outlets can provide a healthy way to cope with stress, manage triggers, and promote self-expression.
- Foster Supportive Relationships: Surround yourself with a supportive network of individuals who understand and respect your journey of recovery. Seek out support groups, counseling, or therapy to connect with others who share similar experiences. Building a community of understanding and encouragement can provide invaluable support on your path to addiction recovery.
Self-care is an essential strategies for addiction recovery, enabling you to nurture your physical, emotional, and mental well-being. By establishing a supportive routine, practicing mindfulness, prioritizing physical and emotional well-being, cultivating healthy coping mechanisms, and fostering supportive relationships, you can empower yourself on the journey to overcoming addiction. Embrace the transformative power of self-care, and unlock your potential for healing, growth, and a brighter future free from addiction.
Deepen Your Journey: Engage in Self-Reflection and Unleash Transformation
Reflection Questions
- What self-care practices resonate with you the most? How do you envision incorporating them into your daily routine?
- Take a moment to identify any potential triggers or challenges you anticipate on your path to addiction recovery. How can self-care strategies help you navigate these obstacles?
- Share one self-care practice that you already engage in or would like to explore further. How has or could this practice positively impact your well-being and recovery?
- Reflect on a time when self-care played a significant role in helping you manage cravings or cope with challenging emotions. What did you learn from that experience, and how can you apply it to your current recovery journey?
Feel free to take your time to reflect on these questions and share your thoughts in the comments section below. Engaging in self-reflection is a powerful step towards incorporating self-care into your strategies for addiction recovery and fostering personal growth.
BUILDING A SOLID FOUNDATION FOR SOBRIETY
Embarking on the journey of addiction recovery can be challenging, but with the right strategies, building a solid foundation for sobriety is a good starting point. In this blog post, we will explore some effective addiction recovery strategies that have helped countless individuals overcome substance abuse and reclaim their lives. Whether you’re just starting your recovery journey or seeking additional tools to support your sobriety, these strategies will provide valuable insights and practical guidance.
- Set Clear and Realistic Goals: Setting clear and realistic goals is essential for addiction recovery. Define what you want to achieve, whether it’s complete abstinence, improved physical and mental health, mending relationships, or pursuing new passions. Break down these goals into smaller, achievable steps to maintain motivation and track progress along the way.
- Seek Professional Support: Seeking professional support is crucial in addiction recovery. Connect with addiction counselors, therapists, or support groups who specialize in substance abuse. They can provide guidance, accountability, and evidence-based techniques tailored to your specific needs. Professional support helps you navigate challenges, address underlying issues, and develop effective coping mechanisms.
- Build a Strong Support System: Surround yourself with a strong support system of friends, family, and individuals who understand and support your recovery journey. Communicate your needs and boundaries to your loved ones and seek their understanding and encouragement. Attend support group meetings or join online communities where you can connect with individuals who have similar experiences, share insights, and offer mutual support.
- Practice Self-Care: Self-care is essential for maintaining sobriety and overall well-being. Prioritize activities that nurture your physical, emotional, and mental health. This can include engaging in regular exercise, adopting healthy eating habits, getting enough restful sleep, practicing mindfulness or meditation, and engaging in hobbies or activities that bring you joy and fulfillment.
- Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Developing healthy coping mechanisms is key to managing cravings, stress, and triggers. Explore techniques such as deep breathing exercises, journaling, practicing gratitude, engaging in creative outlets, or seeking solace in nature. Find healthy alternatives to previous substance use, and be patient and compassionate with yourself as you learn new ways of coping.
By implementing these effective addiction recovery strategies, building a solid foundation for sobriety will help you achieve a healthier, addiction-free life. Remember, recovery is a unique journey, and what works for one person may differ for another. Stay committed, be open to trying new approaches, and seek support when needed. Embrace the transformative power of these strategies and take the first step towards a brighter future of sobriety and well-being.
Please feel free to share your own experience and tips in the comment section
The Reward System and Dopamine
The reward system in the brain is a complex network of structures that are involved in experiencing pleasure and reinforcing behaviors. One of the key neurotransmitters involved in the reward system is dopamine. Dopamine plays a crucial role in signaling pleasure, motivation, and reward.
When we engage in activities that are pleasurable or rewarding, such as eating delicious food or participating in social interactions, the reward system is activated, and dopamine is released in specific brain regions. This release of dopamine creates a sense of pleasure and reinforces the behavior, making us more likely to seek out and repeat those activities.
In the context of addiction, drugs or addictive behaviors can hijack the reward system. Certain substances, such as alcohol or drugs like cocaine or opioids, directly stimulate the release of dopamine in the brain, leading to an intense and immediate pleasurable sensation. This flood of dopamine creates a powerful reinforcement that can drive individuals to continue seeking and using the substance.
Over time, with repeated substance use or engagement in addictive behaviors, the reward system becomes dysregulated. The brain adapts to the excessive dopamine release by reducing the number of dopamine receptors or altering their sensitivity. This leads to a diminished response to natural rewards and an increased drive to seek the addictive substance or behavior to restore dopamine levels to a more normal state.
The relationship between the reward system and dopamine in addiction is complex. Dopamine not only contributes to the initial pleasurable effects of substances or behaviors but also plays a role in the development of tolerance, dependence, and cravings. The dysregulation of the reward system and dopamine function is a significant factor in the cycle of addiction.
Understanding the interplay between the reward system and dopamine helps shed light on why addiction can be so powerful and difficult to overcome. By targeting the reward system and dopamine pathways through various treatment approaches, such as behavioral therapies or medications, it is possible to help restore balance and support recovery.
- Neuroplasticity and Changes in Brain Structure
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to adapt and change in response to experiences and environmental stimuli. It involves the formation and reorganization of neural connections, as well as changes in brain structure.
In the context of addiction, repeated drug use can lead to significant changes in brain structure and function. The brain’s reward system, which is involved in the experience of pleasure and reinforcement, undergoes adaptations in response to the continued presence of drugs.
Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in these changes. With repeated drug use, the brain undergoes structural modifications, such as alterations in the density and functioning of neurons, changes in the release and reuptake of neurotransmitters, and remodeling of neural circuits. These changes can occur in various regions of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and striatum, which are involved in decision-making, emotional regulation, and reward processing.
Over time, these drug-induced changes in brain structure can contribute to the development of addiction. They can lead to a heightened sensitivity to drug-related cues, impaired cognitive control, and increased cravings. Additionally, neuroplasticity can also play a role in the recovery process, as the brain has the capacity to rewire and regain normal functioning with abstinence from drugs and the adoption of healthy behaviors.
Understanding the relationship between neuroplasticity and changes in brain structure is important as it highlights the impact of addiction on the brain and emphasizes the potential for recovery and healing through interventions that promote neuroplasticity, such as therapy, cognitive rehabilitation, and engaging in healthy activities.
- Factors Influencing Addiction Vulnerability
Factors influencing addiction vulnerability can vary from person to person and can be a combination of genetic, environmental, and individual factors. Here are some key factors that can contribute to a person’s vulnerability to addiction:
Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role in addiction vulnerability. Certain individuals may have a genetic predisposition that makes them more susceptible to developing addictive behaviors when exposed to drugs or alcohol. Genetic variations can affect how substances interact with the brain, impacting the reward system and increasing the risk of addiction.
Environmental Factors: The environment in which a person grows up and lives can greatly influence their addiction vulnerability. Factors such as peer influence, family history of addiction, exposure to drugs or alcohol, and socioeconomic status can all contribute to an individual’s susceptibility to addiction.
Co-occurring Mental Health Disorders: People with underlying mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, or trauma-related disorders, have a higher risk of developing addiction. Substance use can be a way to self-medicate or cope with these mental health issues, leading to a cycle of addiction.
Childhood Trauma: Childhood experiences, such as physical, emotional, or sexual abuse, neglect, or other traumatic events, can significantly impact addiction vulnerability. Trauma can alter brain development, emotional regulation, and coping mechanisms, increasing the likelihood of substance abuse as a means of escape or self-soothing.
Social and Peer Influence: The influence of friends, family, and social networks can play a role in addiction vulnerability. Peer pressure, social acceptance of substance use, and exposure to substance-using environments can all contribute to the initiation and maintenance of addictive behaviors.
Stress and Coping Mechanisms: Chronic stress can increase the risk of addiction. Some individuals may turn to drugs or alcohol as a way to cope with stress, seeking temporary relief or escape. Unhealthy coping mechanisms can develop into addictive patterns over time.
It’s important to note that while these factors can increase vulnerability to addiction, they do not guarantee that an individual will develop an addiction. The interplay of these factors can vary, and personal choices, support systems, and access to resources also play a significant role in determining addiction outcomes.
- Addiction as a Treatable Medical Condition
Addiction is now widely recognized as a treatable medical condition rather than a moral failing or lack of willpower. Here’s a clear and concise explanation of addiction as a treatable medical condition:
Definition of Addiction: Addiction is a chronic disease characterized by compulsive drug or alcohol use despite negative consequences. It affects the brain’s reward system, leading to intense cravings and a loss of control over substance use.
Brain Changes: Addiction causes significant changes in the brain’s structure and function. Prolonged substance abuse alters the brain’s communication pathways, affecting decision-making, impulse control, and judgment. These changes make it challenging for individuals to quit using drugs or alcohol without proper treatment.
Medical Perspective: Addiction is now recognized as a medical condition by major medical and psychiatric associations, including the American Medical Association (AMA) and the American Psychiatric Association (APA). It is classified as a substance use disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5).
Treatable Condition: Just like other chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, addiction can be effectively treated. Treatment approaches may include a combination of medications, behavioral therapies, counseling, and support services.
Recovery and Management: With appropriate treatment and support, individuals with addiction can achieve long-term recovery. Recovery is a process that involves learning new coping skills, addressing underlying issues, and making positive lifestyle changes. It’s important to understand that recovery is a lifelong journey, and ongoing support is often necessary.
Holistic Approach: Treating addiction as a medical condition involves adopting a holistic approach that addresses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of the individual. Treatment focuses not only on stopping substance use but also on improving overall well-being and quality of life.
Importance of Professional Help: Seeking professional help is crucial for the effective management of addiction. Medical professionals, addiction specialists, therapists, and support groups can provide evidence-based treatments, counseling, and support tailored to the individual’s needs.
Destigmatizing Addiction: Recognizing addiction as a treatable medical condition helps to reduce the stigma surrounding it. Education, awareness campaigns, and open conversations about addiction are essential for promoting empathy, understanding, and support for individuals seeking help.
In conclusion, addiction is a treatable medical condition that affects the brain and behavior. With proper treatment, support, and a comprehensive approach, individuals with addiction can lead fulfilling lives in recovery.
- Breaking Down Stigmas and Promoting Empathy
Breaking down stigmas surrounding addiction involves challenging the common misconceptions and negative judgments associated with it. Many people still view addiction as a moral failing, a lack of willpower, or a choice made by individuals. However, it’s important to recognize that addiction is a complex medical condition that affects the brain and behavior. It is not simply a matter of weak character or lack of self-control.
One of the most effective ways to break down stigmas is through education. By providing accurate information about addiction, its causes, and its impact on individuals, we can help dispel myths and misconceptions. This includes understanding that addiction is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Education helps people realize that addiction can happen to anyone, regardless of their background or social status.
Promoting empathy goes hand in hand with breaking down stigmas. It involves cultivating a deeper understanding and compassion for individuals facing addiction. Empathy means recognizing that addiction is not a personal choice but a medical condition that requires support and treatment. It requires putting ourselves in the shoes of those affected by addiction and striving to understand their struggles, emotions, and experiences without judgment.
Creating an empathetic environment involves offering support and understanding to individuals affected by addiction. It means listening to their stories, acknowledging their challenges, and providing assistance without blame or shame. Empathy involves treating individuals with respect, dignity, and kindness, fostering an environment where they feel safe to seek help and share their experiences.
To break down stigmas and promote empathy effectively, open and honest conversations about addiction are crucial. Encouraging dialogue helps reduce the fear and shame associated with addiction. It allows individuals to share their experiences, challenges, and successes, creating a sense of community and understanding. By challenging discriminatory language and attitudes, we can foster a culture of acceptance and support.
In summary, breaking down stigmas and promoting empathy is about recognizing addiction as a complex medical condition and fostering a compassionate and understanding society. Education, empathy, and open conversations play key roles in reducing stigma, supporting individuals affected by addiction, and creating a path toward recovery and healing.
In conclusion, understanding addiction is crucial for addressing this complex medical condition and supporting those affected by it. Throughout this article, we have explored the science of addiction, including its impact on the brain, the role of the reward system and dopamine, neuroplasticity, addiction vulnerability factors, and the treatability of addiction as a medical condition.